In June 2021, Web of Science (Clarivate Analytics) released their 2020 JCR Impact Factor. Aging is pleased to report that our 2020 impact factor is 5.682.
Aging (Aging-US) Research
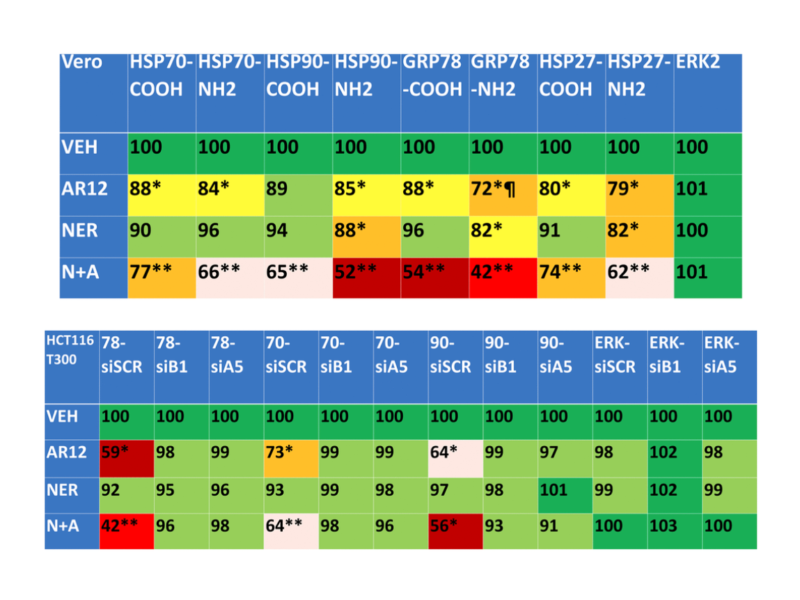
Researchers tested antiviral, anticancer, and immunosuppressive drug combinations that may aid in treating neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease.

From the University of California Berkeley and Apheresis Care Group, researchers discovered a method of “refreshing” blood that reverses some of the effects of aging.
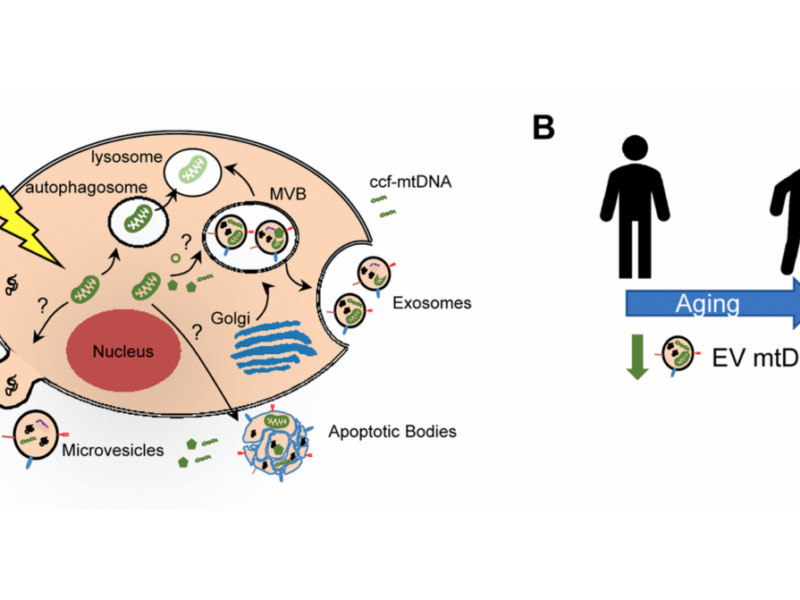
Authors from the National Institute on Aging wrote the editorial paper, “Mitochondria as extracellular vesicle cargo in aging.”
Researchers from the Campisi Lab discovered new insights while investigating Cdkn1a transcript variants 1 and 2.
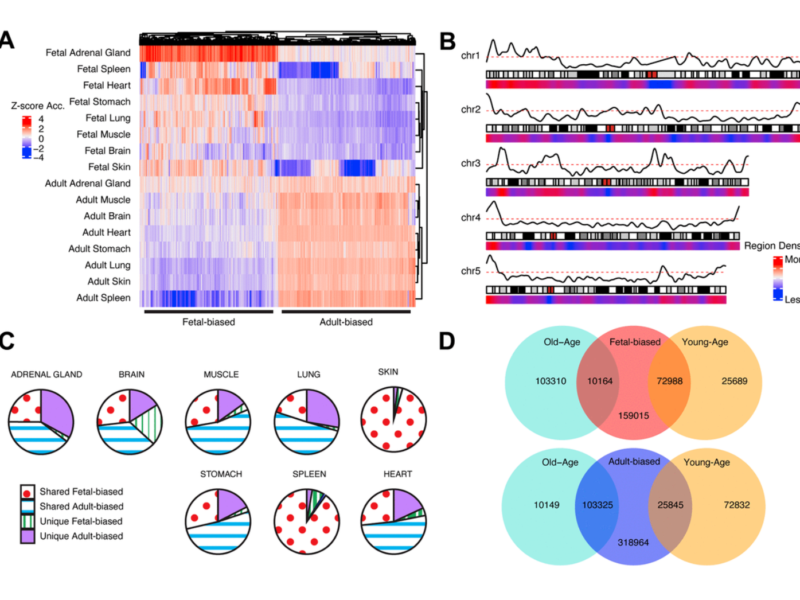
Researchers from Harvard University and the Broad Institute wrote a theory article, published by Aging in 2021, and entitled, “Shifting epigenetic contexts influence regulatory variation and disease risk.”
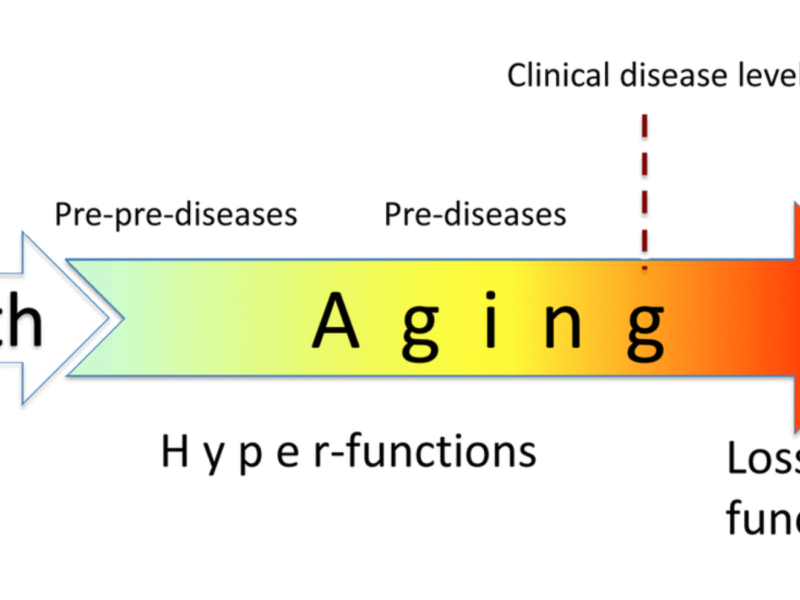
In 2018, Dr. Mikhail Blagosklonny wrote a thought provoking theory article, entitled: “Disease or not, aging is easily treatable.”
What was found buried in the dirt on Easter Island in 1964 was a compound that would mystify aging researchers for the next 50 years.

Researchers trained and validated a deep learning neural network technology—the GeroSense Biological Age Acceleration (BAA) system—to extract health-associated features from wearable sensor data.
![Figure 1. The EORS downward spiral of aging and Alzheimer’s (Epigenetic Oxidative Redox Shift) [2]. Yellow arrows illustrate mechanistic targets that propel the vicious cycle triggered by age-related oxidative shifts (NAD+/NADH) and age-related sedentary behavior, which elicit ROS, inflammatory stress and possibly Aβ. Green arrows indicate practical interventions to decelerate the vicious cycle and impede the progression of aging and AD.](https://aging-us.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/Screen-Shot-2021-06-24-at-4.49.30-PM-800x600.png)
In a trending Aging editorial paper, researchers explain that switches in the aging process may be a window of opportunity for patients with Alzheimer’s disease and potential epigenetic treatments.

