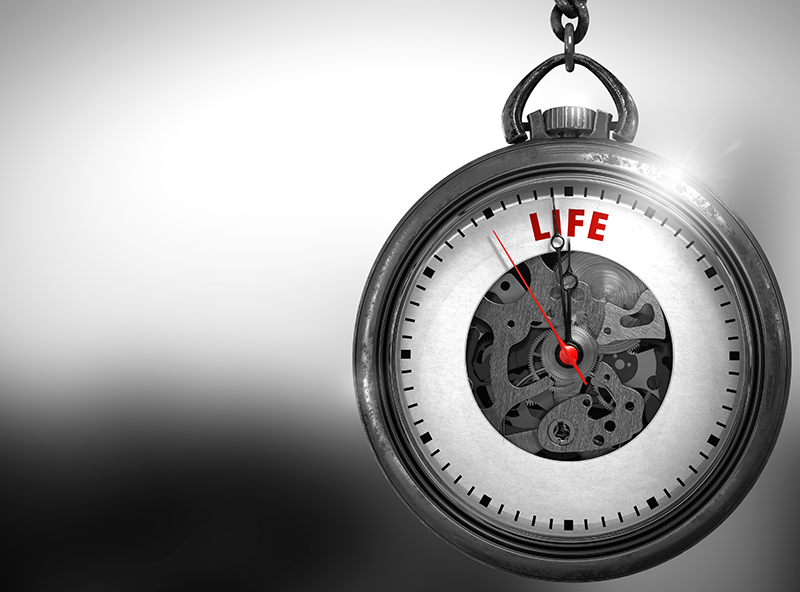
Researchers analyzed the behavior of hybrid mice and presented a novel method to qualitatively estimate natural lifespan.
Aging-US Research
In a priority research paper published by Aging-US in January of 2022, researchers investigated aged muscle stem cells and their ability to sense and respond to mechanical cues.
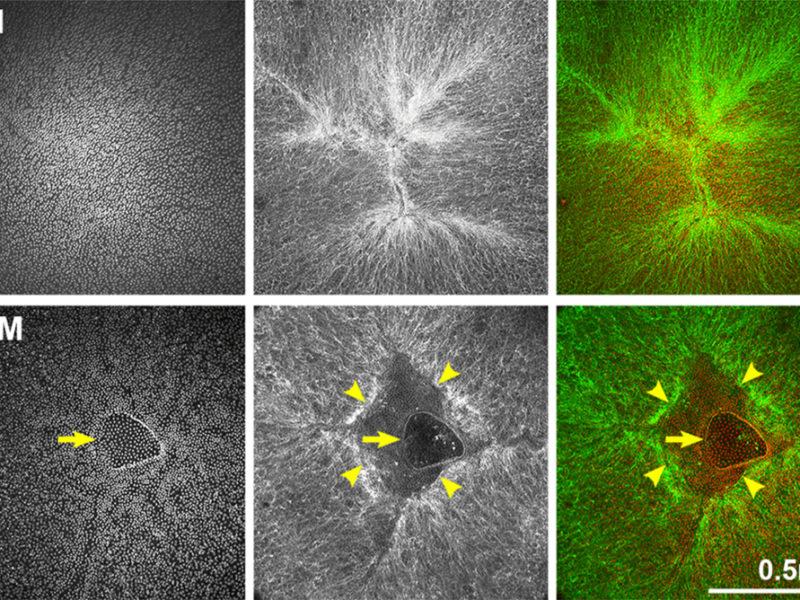
In this 2019 study, researchers examined murine models to determine common age-related eye lens changes that contribute to eventual vision impairment and loss.
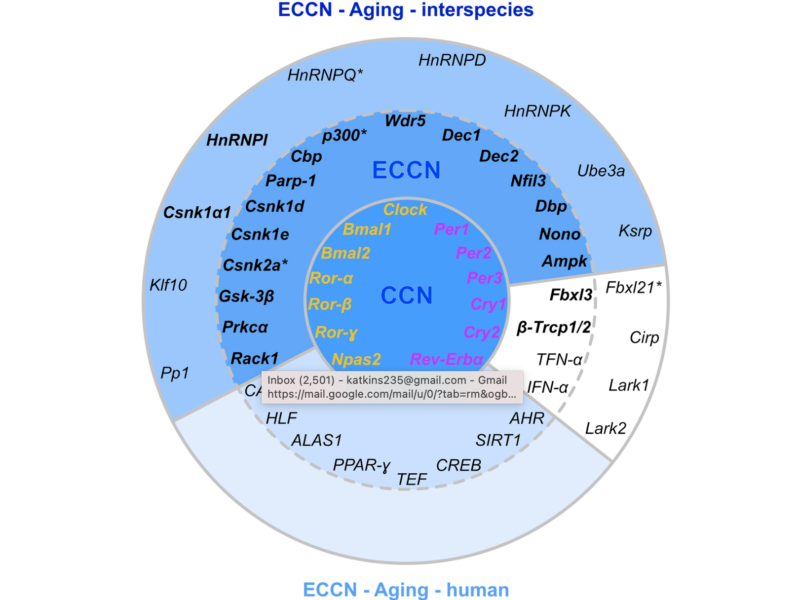
In the cover paper published in Aging (Aging-US) Volume 13, Issue 24, researchers conducted a study suggesting that the circadian system is subjected to aging-related gene alterations.
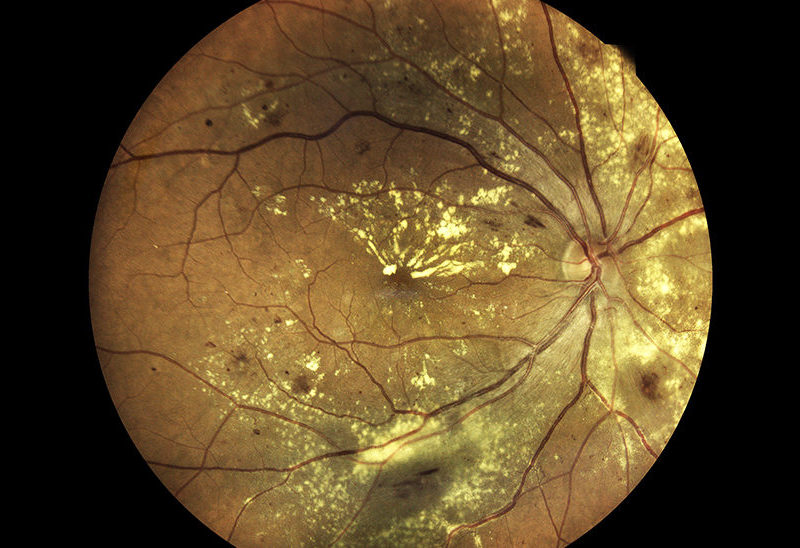
Over 15 million people in the United States are currently struggling with age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Researchers investigated a mechanism of AMD pathophysiology.
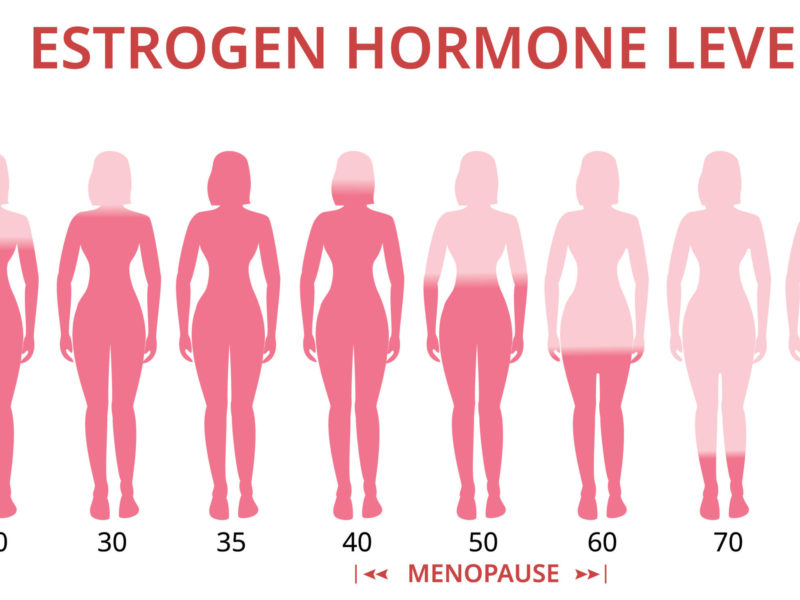
As a continuation of a previous study, researchers evaluated the effects of estrogen suppression, followed by estradiol supplementation, on biological age measured by glycan age.

After taking Rejuvant® for approximately 7 months, a recent study revealed that participants experienced an average 8 year reduction in biological aging.
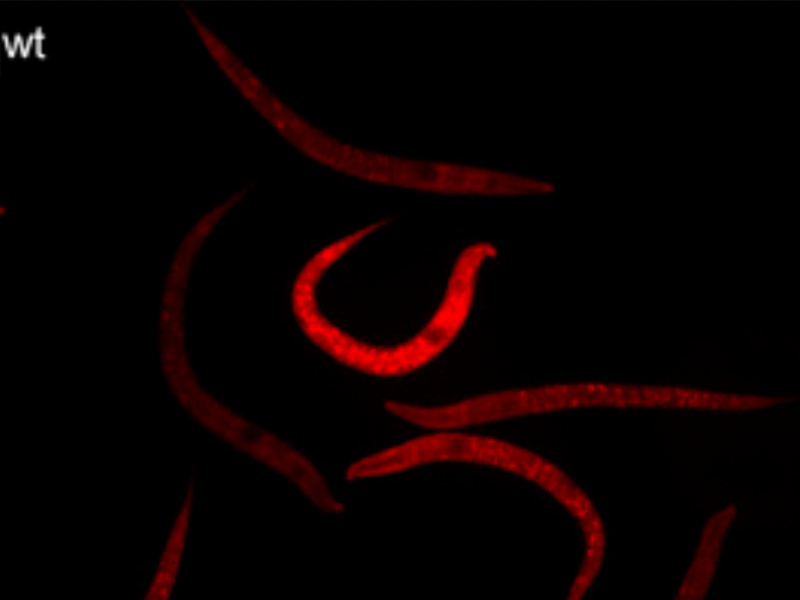

Researchers examined roundworms to determine the role of mitochondrial dysfunction in progressive neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease.

In a two-year study, researchers compared the effects of choral singing with the effects of health education in an elderly cohort.

Machine learning and a broad range of biochemical and physiological traits were used to develop a new composite metric as a potential proxy for an underlying whole-body aging mechanism.

