Aging has long been explained in different ways. One traditional view is that it results from the gradual accumulation of molecular damage over time. Another perspective, based on evolutionary theory, suggests that natural selection strongly protects health during youth and reproductive years but becomes less effective later in life.
Aging-US Research

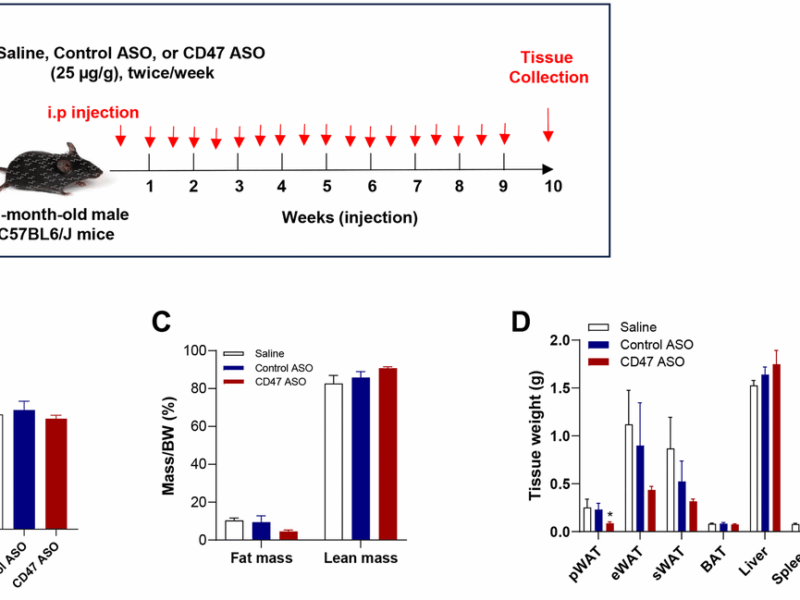
Since the first description of replicative senescence triggered by telomere shortening in the 1960s, other stressors such as mitochondrial dysfunction and DNA damage were shown to induce senescence in vitro. In vivo, senescent cells show both beneficial physiological and harmful pathological roles, yet their contribution to aging and disease remain incompletely understood.

While maternal health has traditionally been central to research on pregnancy and child development, there is growing recognition that paternal factors also play a role, particularly the father’s age. Several studies have found a modest increase in risk of neurodevelopmental conditions, including autism spectrum disorder, among children born to older fathers. However, the biological mechanisms underlying this association are still not fully understood.

While chocolate and coffee have been associated with better health outcomes, pinpointing the responsible specific compounds has been difficult. These foods contain multiple bioactive substances that are often consumed together, and few studies have explored their individual effects on the human epigenome, the system of chemical modifications that control gene activity and change with age.

The results of studies revealed in this paper indicate that advanced paternal age increases the risk of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in children, potentially due to sperm epigenetic changes.

As we age, every tissue in the body undergoes gradual molecular changes. A long-standing question in aging research is whether these changes follow common patterns across tissues or whether each tissue ages on its own.
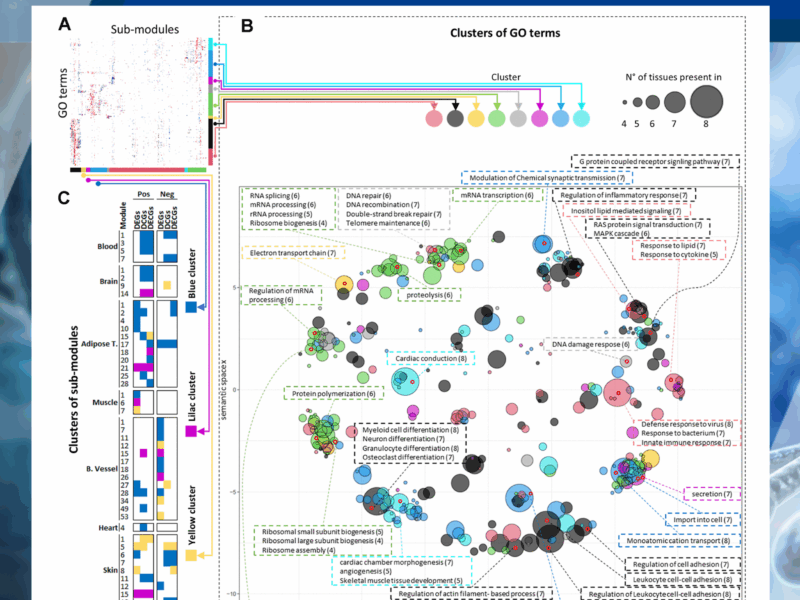
Although transcriptomic changes are known to occur with age, the extent to which these are conserved across tissues is unclear. Previous studies have identified little conservation in age-modulated genes in different tissues. Here, we sought to identify common transcriptional changes with age in humans (aged 20 to 70) across tissues using differential network analysis, assuming that differential expression analysis alone cannot detect all changes in the transcriptional landscape that occur in tissues with age.