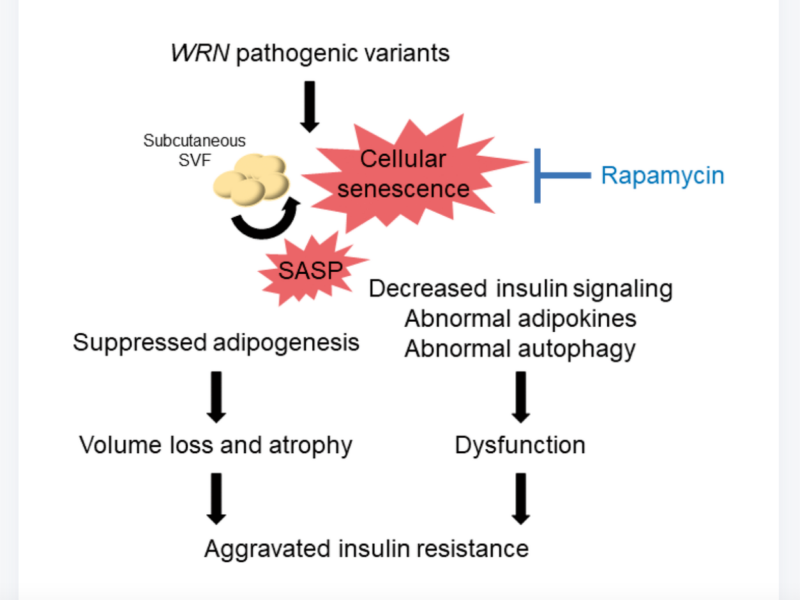
In this new study, researchers from Japan investigated the molecular mechanisms of subcutaneous fat dysfunction in Werner syndrome.
Aging (Aging-US) Research

Dr. Mikhail Blagosklonny joins “Master One Thing” host Krister Kauppi to discuss the impact of his rapamycin research and hyperfunciton theory of aging.
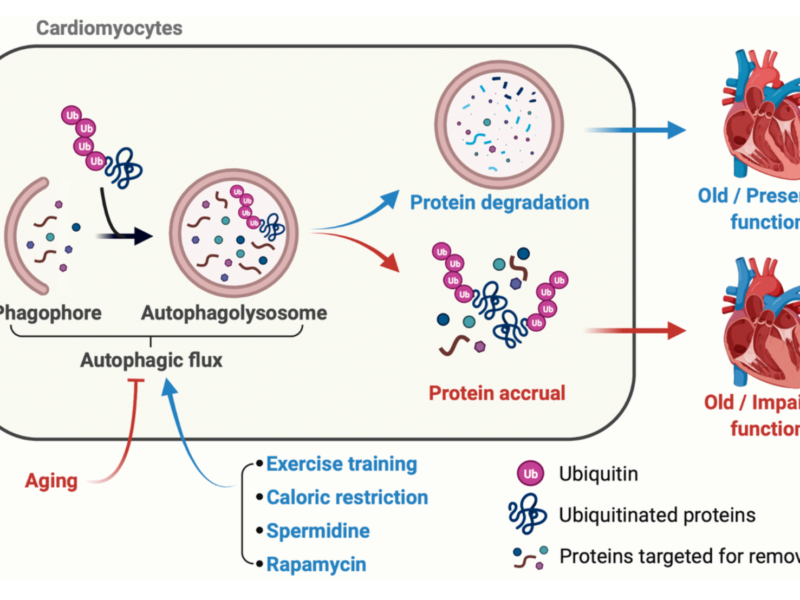
In a new research perspective, researchers discuss spermidine, rapamycin, caloric restriction, and exercise training to improve cardiac health in aging individuals.
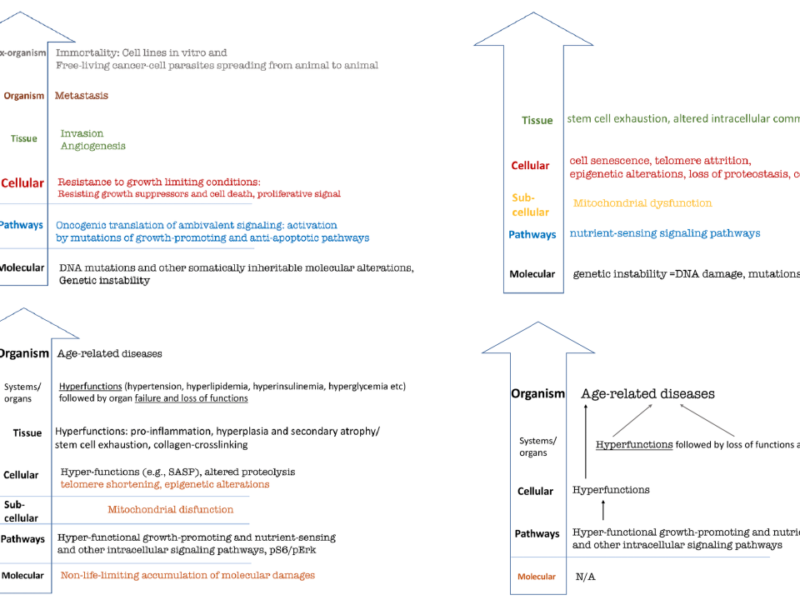
Dr. Mikhail Blagosklonny published an original review paper in Aging (Aging-US) Volume 14, Issue 9, entitled, “Hallmarks of cancer and hallmarks of aging.”
Mikhail Blagosklonny, M.D., Ph.D., has a recommendation for Altos Labs in his new research perspective, entitled, “Altos Labs and the quest for immortality: but can we live longer right now?”
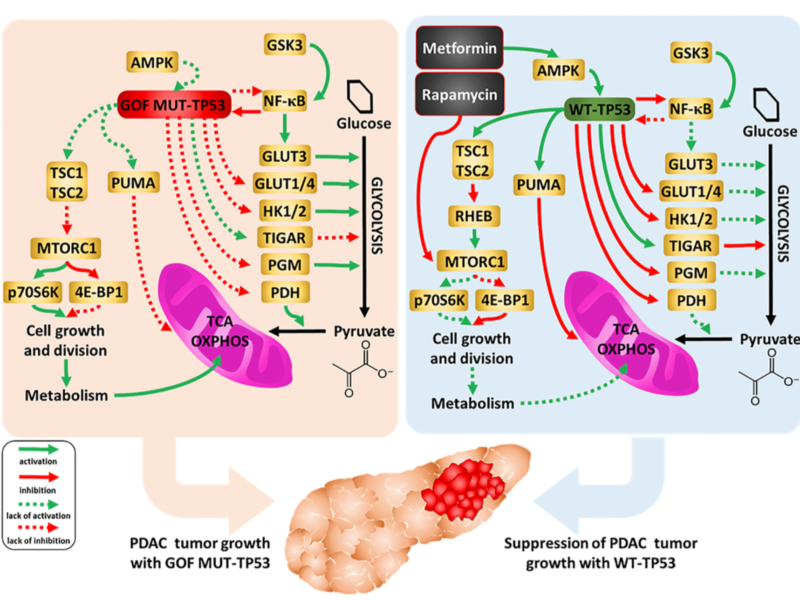
In Aging’s Volume 14, Issue 8, cover paper, researchers found that the restoration of wild-type TP53 decreased pancreatic cancer cell resistance to various drugs, including rapamycin.
Researchers investigated radiation-induced senescent cells and their effects on tumor growth, and senotherapeutics to mitigate these effects.
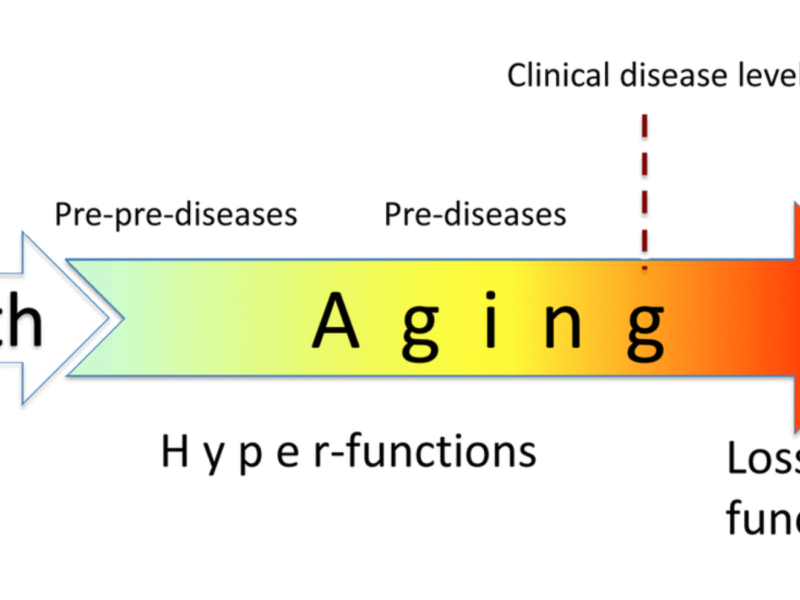
In 2018, Dr. Mikhail Blagosklonny wrote a thought provoking theory article, entitled: “Disease or not, aging is easily treatable.”
What was found buried in the dirt on Easter Island in 1964 was a compound that would mystify aging researchers for the next 50 years.

In an effort to mimic metformin and rapamycin, researchers used powerful screening methods to analyze over 800 natural compounds to assess their anti-aging potential and safety profile.