The Trending with Impact series highlights Aging publications that attract higher visibility among readers around the world online, in the news, and on social media—beyond normal readership levels. Look for future science news about the latest trending publications here, and at Aging-US.com.
—
Heat shock proteins (HSPs), also known today as stress proteins, were first observed in fruit flies in the 1960s. After Dr. Ferruccio Ritossa inadvertently subjected a preparation of fruit fly salivary glands to a non-lethal increase in temperature, he discovered a new pattern of chromosomal “puffing.” In 1974, researchers identified the proteins that were encoded by the “puffs” recorded by Dr. Ritossa, and named them heat shock proteins.
These newfound proteins appeared to only become detectable when the cells were heated. Researchers later learned that HSPs can also be induced by exposure to oxidants, toxins, heavy metals, free radicals, viruses, and other stressors. Since its discovery, variations of this genetic system have been found in all bacteria, plants, and animals. HSPs have been well-studied since this revelation, and researchers now believe these molecular chaperones play important roles in protein refolding, aging-related diseases, and overall longevity.
“Toxic misfolded proteins are key drivers of AD [Alzheimer’s disease], ALS [Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis], HC [Huntington’s Chorea] and other neurodegenerative diseases.”
Researchers from Virginia Commonwealth University, Translational Genomics Research Institute, and the Banner Alzheimer’s Institute took part in a research study experimenting with combinations of therapeutic agents which they believe may improve neurodegenerative disorders. In 2021, their paper was published in Aging’s Volume 13, Issue 13, and entitled, “Inhibition of heat shock proteins increases autophagosome formation, and reduces the expression of APP, Tau, SOD1 G93A and TDP-43.”
“In this paper we examined using isogenic colon cancer cells [with] several existing drugs that function by increasing autophagy and degrading misfolded proteins.”
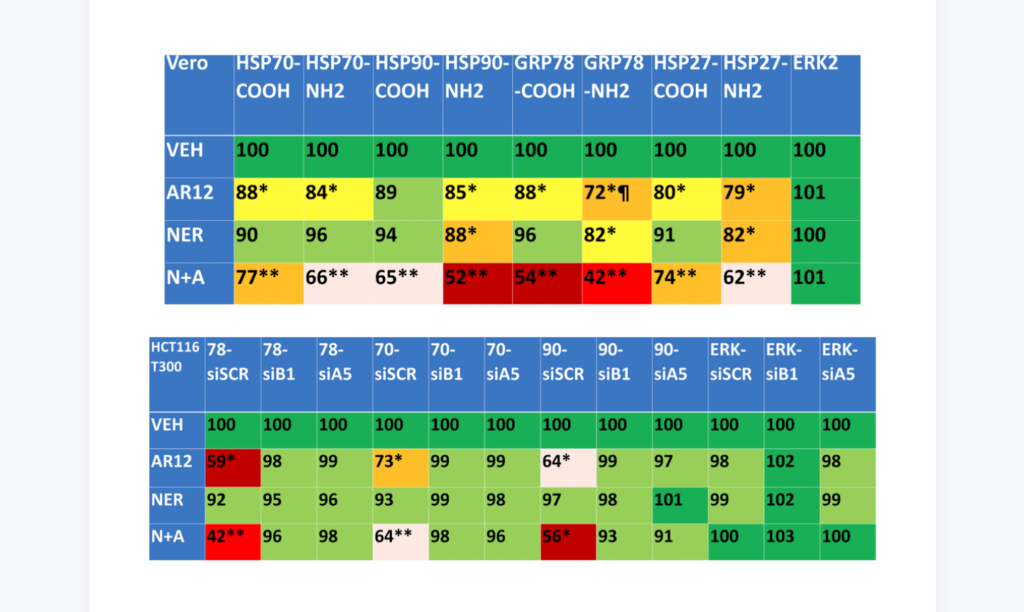
The Study
“Aberrant expression of chaperone proteins is found in many human pathologies including cancer, in virology and in AD, ALS and HC.”
In this study, researchers tested drugs that have been used preclinically and clinically in several anticancer studies. The drugs used were: AR12, an antiviral chaperone ATPase inhibitor; Neratinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor; a combination of AR12 and Neratinib; Fingolimod, an immunosuppressive sphingosine l-phosphate receptor modulator; MMF, monomethyl fumarate; and a combination of Fingolimod and MMF.
The cells they tested these drug combinations on in vitro included Vero cells (African Green Monkey kidney cells), isogenic HCT116 colon cancer cells (genetically manipulated colon cancer cells), and GBM6 cells (glioblastoma cancer stem cells). They also used plasmids, antibodies, and siRNAs. Researchers acknowledged that the use of non-neuronal cells may be a limitation of this study.
“Our present studies were performed in non-neuronal cells and as a caveat, it is possible that our data in HCT116 and Vero cells will not be reflective of the same processes in neuronal cells.”
Despite this caveat, results from their research were promising. Some combinations of these drugs were capable of knocking down many disease specific proteins that form toxic aggregates inside cells and in extracellular environments via autophagy.
Conclusion
“As the mechanism of drug-action became clearer it was apparent that these agents should also be tested in neurodegenerative diseases. The entire neurodegenerative field needs rapid translational methods that target the underlying cause of disease, toxic misfolded protein. The findings from this work warrant further testing with a focus on clinical utility.”
Click here to read the full research paper, published by Aging.
WATCH: MORE AGING VIDEOS ON LABTUBE
—
Aging is an open-access journal that publishes research papers monthly in all fields of aging research and other topics. These papers are available to read at no cost to readers on Aging-us.com. Open-access journals offer information that has the potential to benefit our societies from the inside out and may be shared with friends, neighbors, colleagues, and other researchers, far and wide.
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].