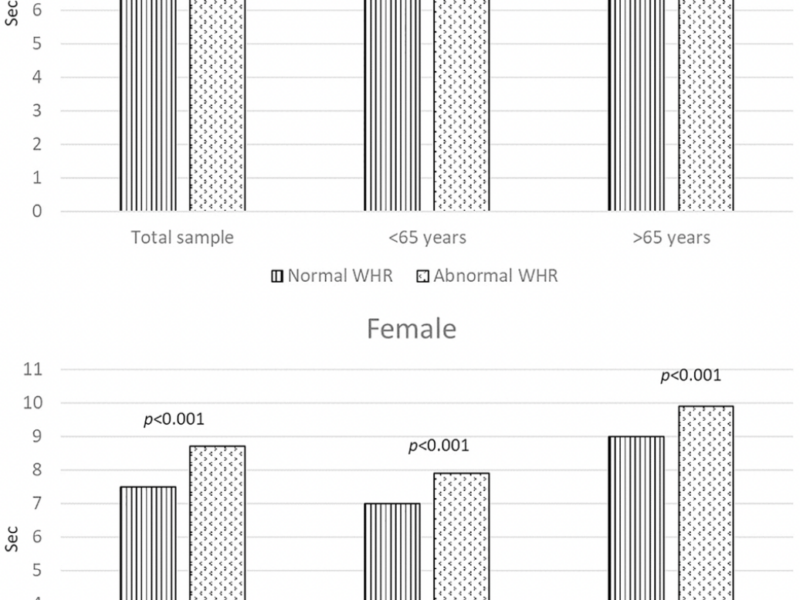
Aging-US Research
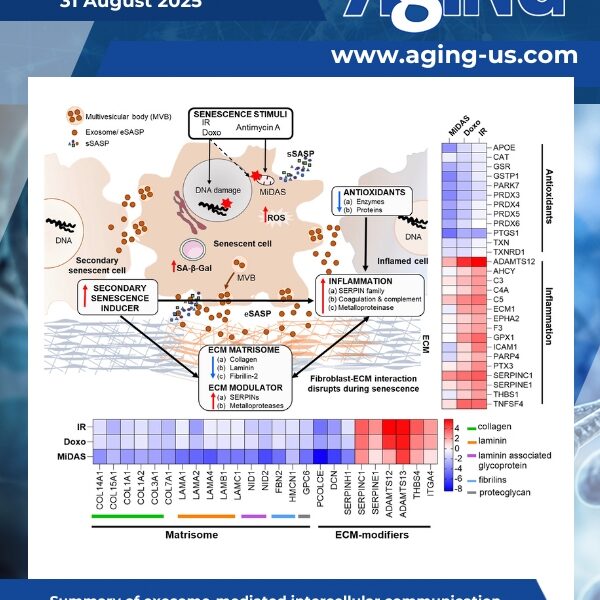
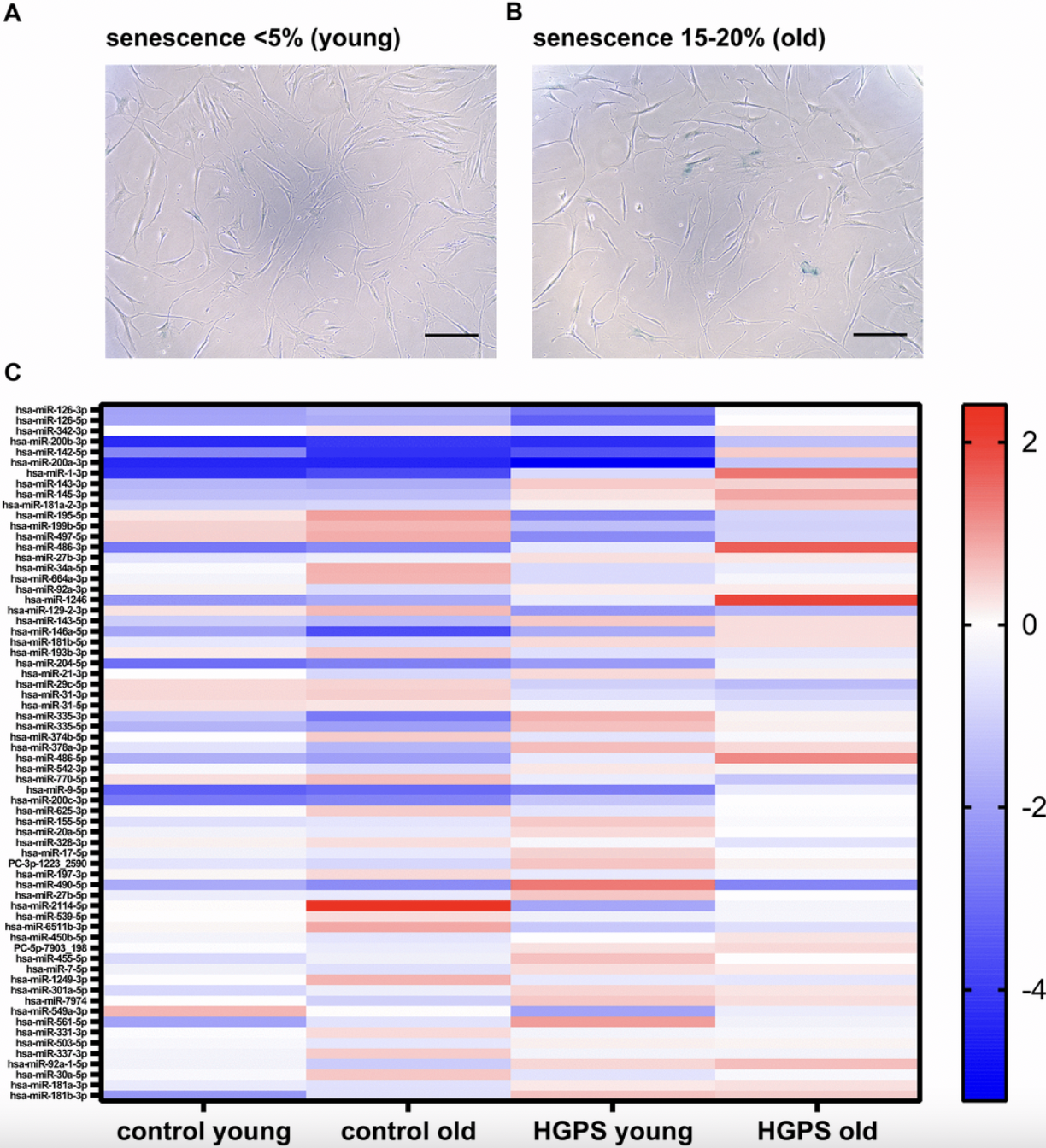
Senescence emerged as significant mechanism of aging and age-related diseases, offering an attractive target for clinical interventions. Senescent cells release a senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), including exosomes that may act as signal transducers between distal tissues, and propagate secondary senescence.
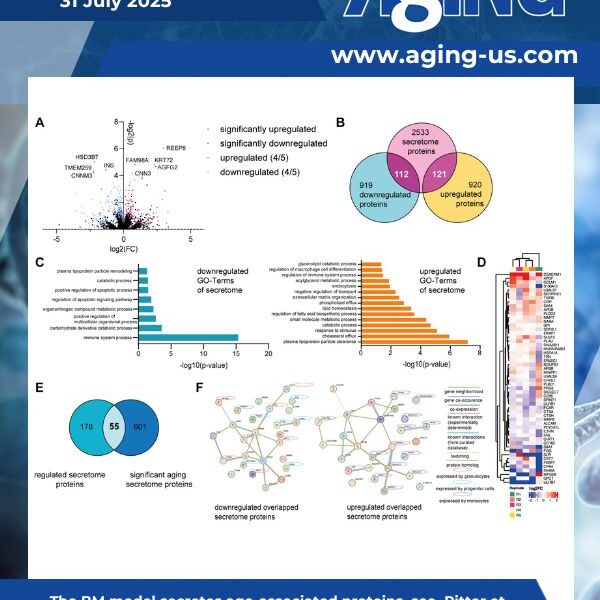
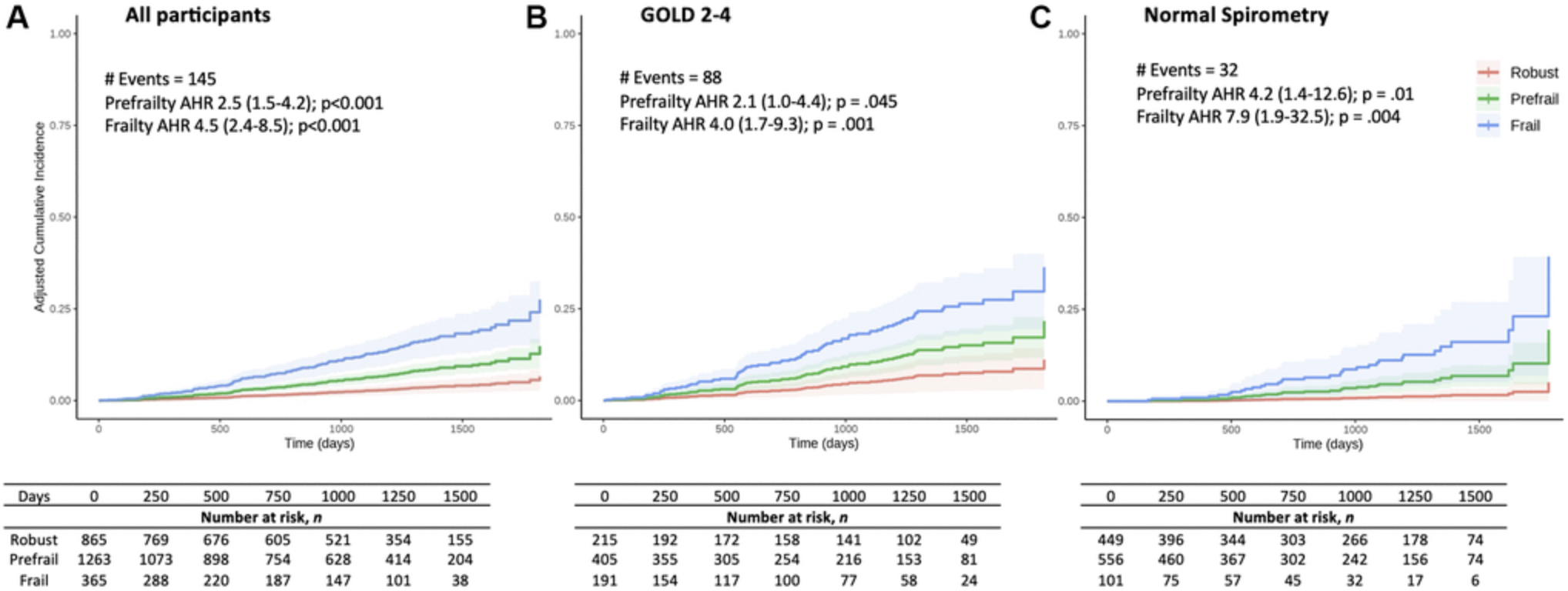
Aging is a complex process that significantly contributes to age-related diseases and poses significant challenges for effective interventions, with few holistic anti-aging approaches successfully reversing its signs.
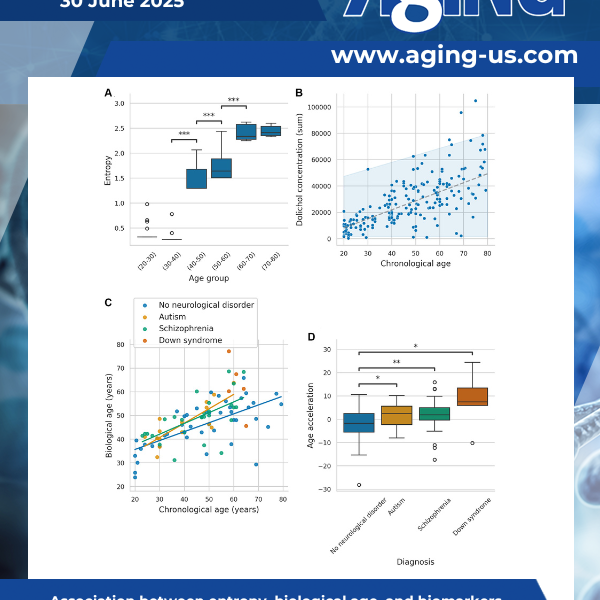
This study introduces DoliClock, a lipid-based biological aging clock designed to predict the age of the prefrontal cortex using post-mortem lipidomic data. Significant age acceleration was observed in autism, schizophrenia, and Down syndrome.