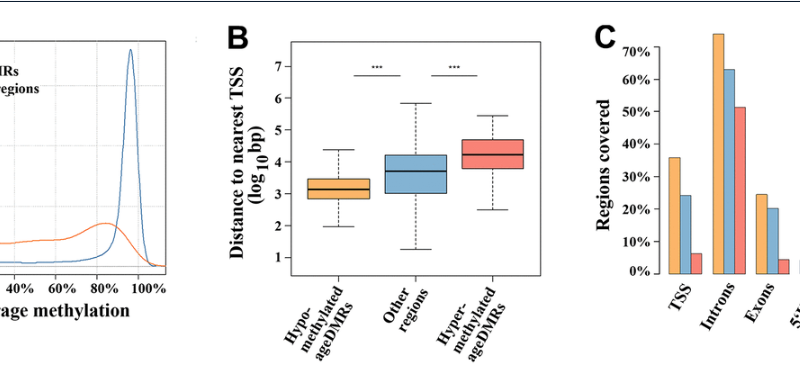
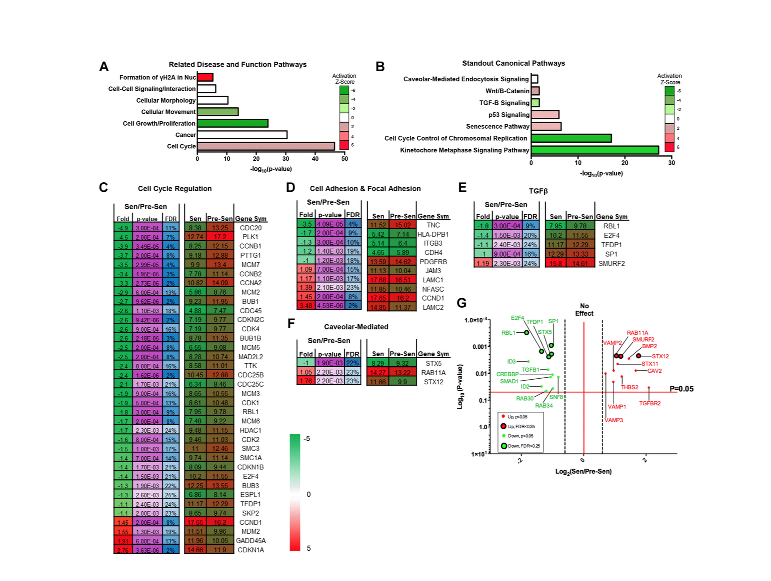
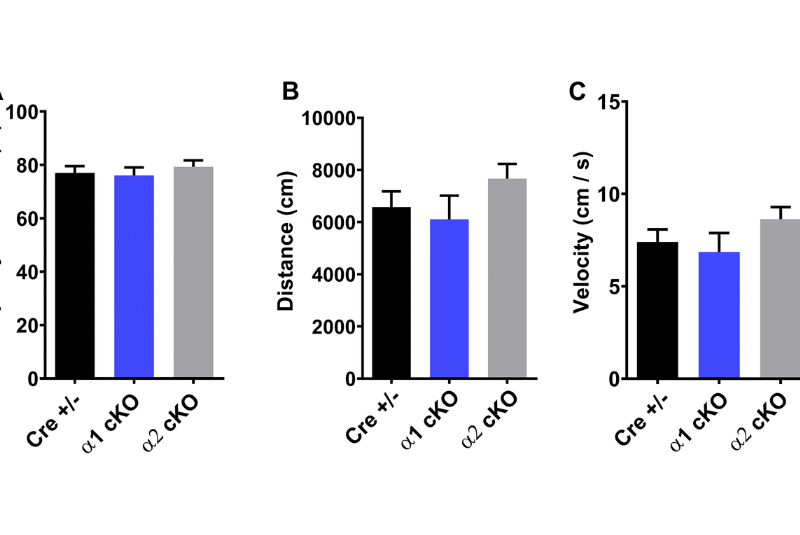
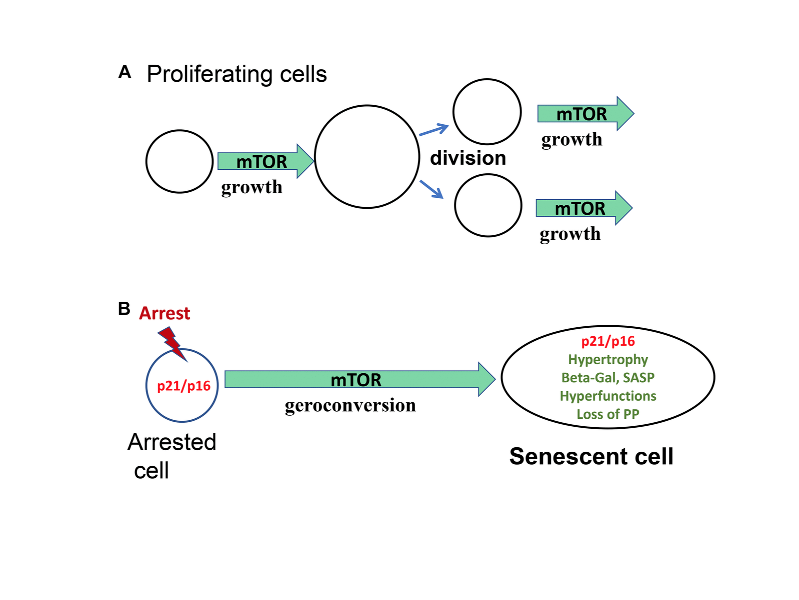
Aging-US Research
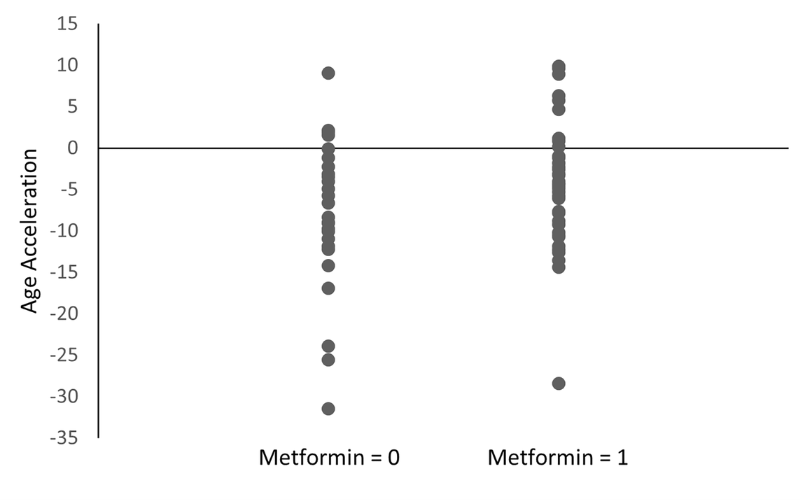
Telomere length (TL) has been reported to be associated with depression and cognitive impairment in elderly. Early detection of depression and cognitive impairment is important to delay disease progression. Therefore, researchers aimed to identify whether TL is associated with early subjective depressive symptoms and cognitive complaints among healthy elderly subjects…
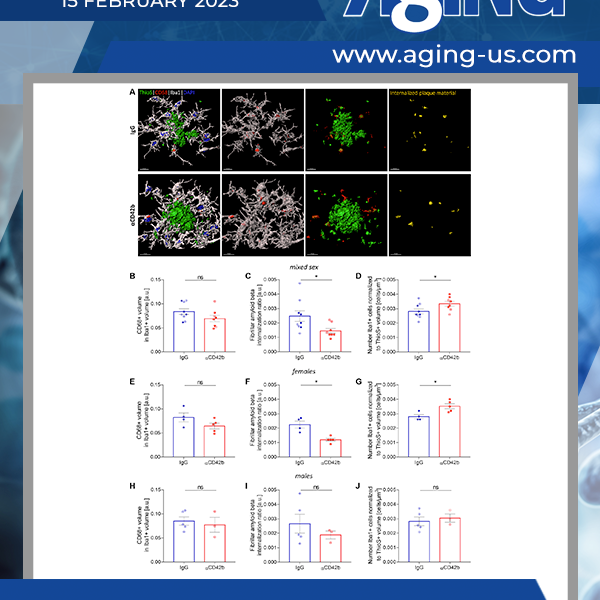
In Alzheimer’s disease (AD), platelets become dysfunctional and might contribute to amyloid beta deposition. Here, the researchers depleted platelets in one-year-old APP Swedish PS1 dE9 (APP-PS1) transgenic mice for five days, using intraperitoneal injections of an anti-CD42b antibody, and assessed changes in cerebral amyloidosis, plaque-associated neuritic dystrophy and gliosis…
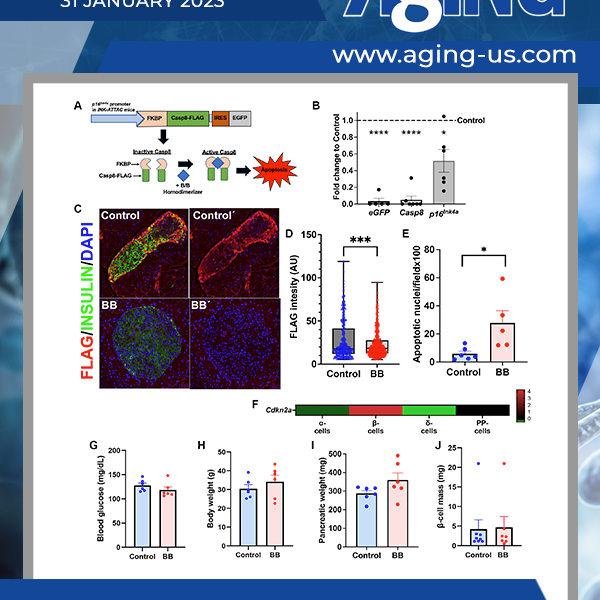
Type 2 diabetes is partly characterized by decreased β-cell mass and function which have been linked to cellular senescence. Despite a low basal proliferative rate of adult β-cells, they can respond to growth stimuli, but this proliferative capacity decreases with age and correlates with increased expression of senescence effector, p16Ink4a.