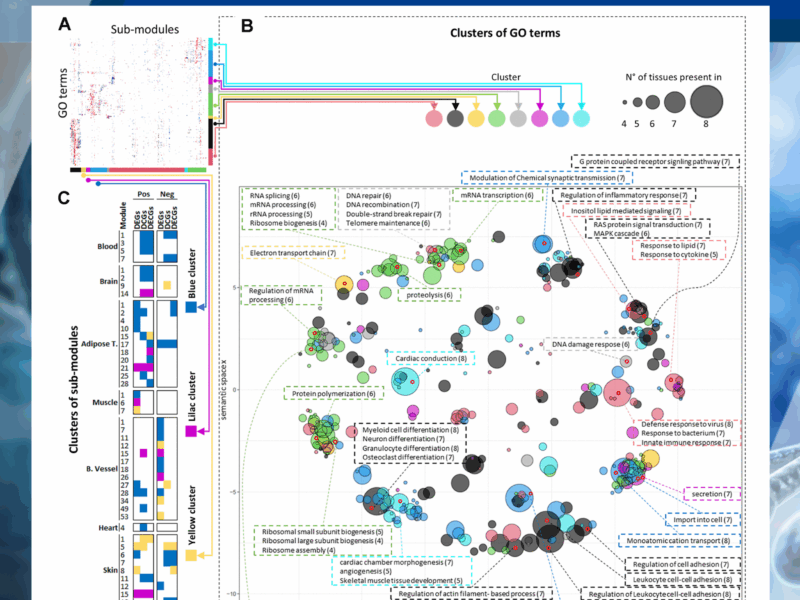
Although transcriptomic changes are known to occur with age, the extent to which these are conserved across tissues is unclear. Previous studies have identified little conservation in age-modulated genes in different tissues. Here, we sought to identify common transcriptional changes with age in humans (aged 20 to 70) across tissues using differential network analysis, assuming that differential expression analysis alone cannot detect all changes in the transcriptional landscape that occur in tissues with age.
Aging-US Research
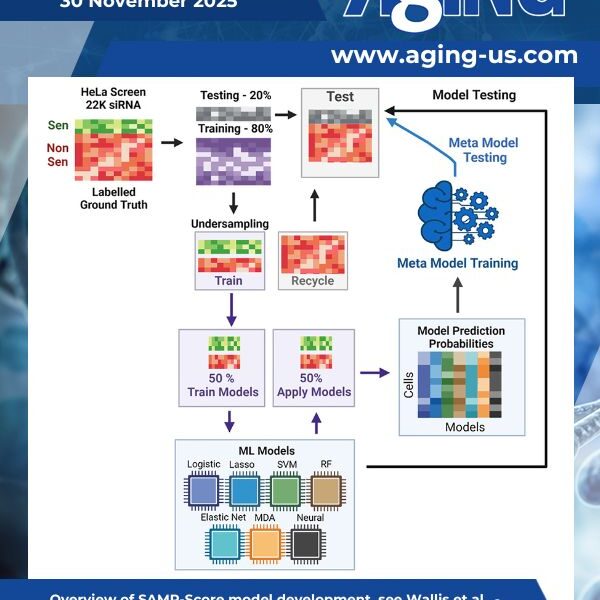
Senescence identification is rendered challenging due to a lack of universally available biomarkers. This represents a bottleneck in efforts to develop pro-senescence therapeutics – agents designed to induce the arrest of cellular proliferation associated with a senescence response in cancer cells for therapeutic gain.
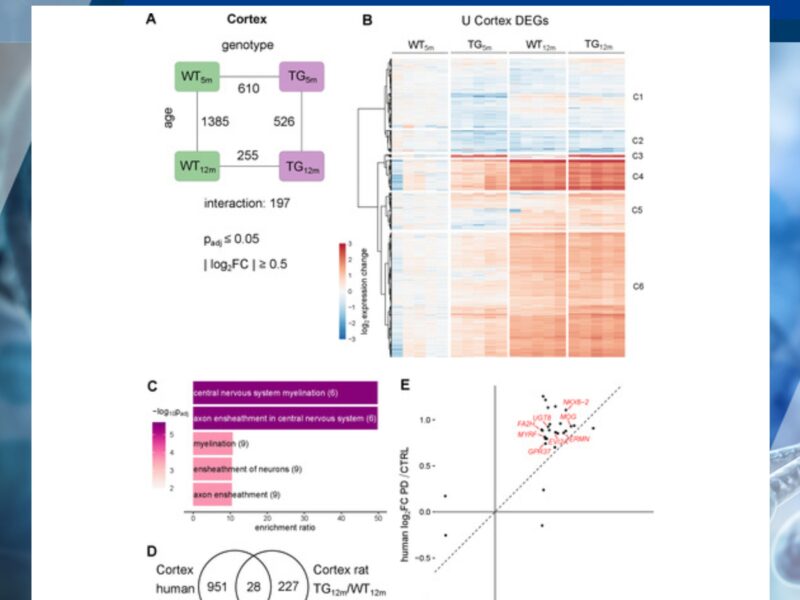
Synucleinopathies are age-dependent neurodegenerative diseases characterized by alpha-synuclein accumulation with distinct vulnerabilities across brain regions. Understanding early disease stages is essential to uncover initial molecular changes that might enable earlier diagnosis and causal therapy.
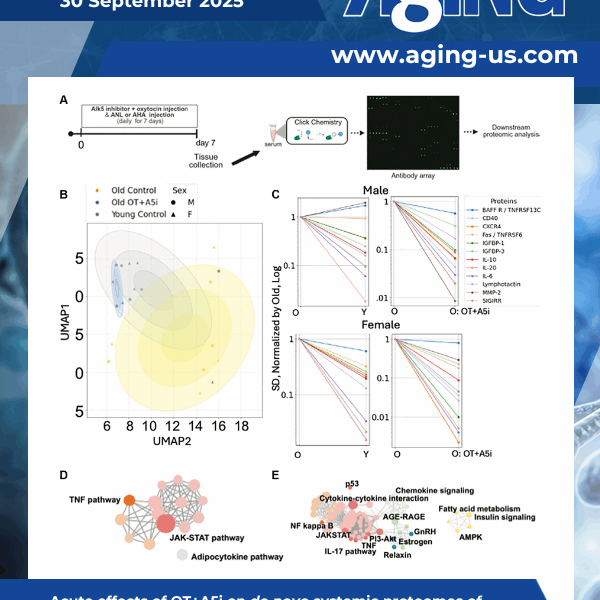
Here, we examined whether simultaneous calibration of pathways that change with aging in opposite directions would be more effective in increasing healthspan and lifespan. Moreover, we started with the challenging age group – frail 25-months-old mice that are equivalent to ~75-year-old people.