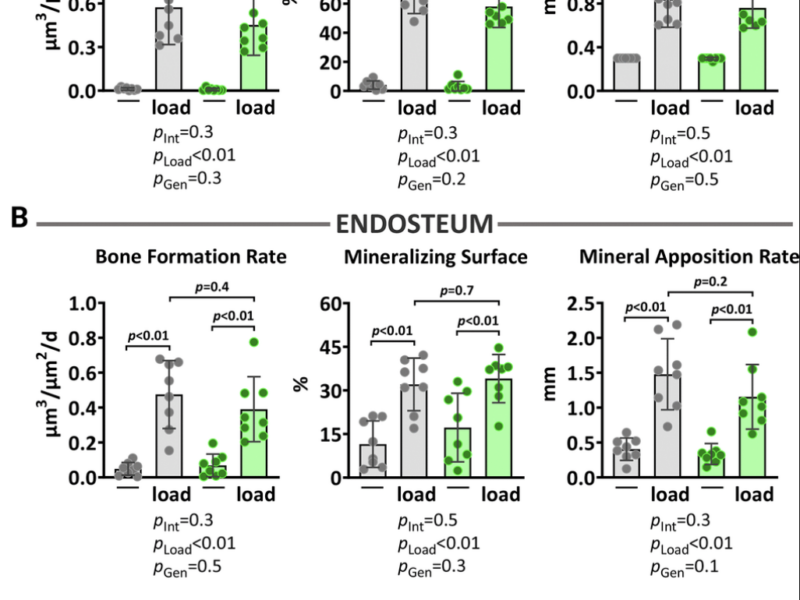
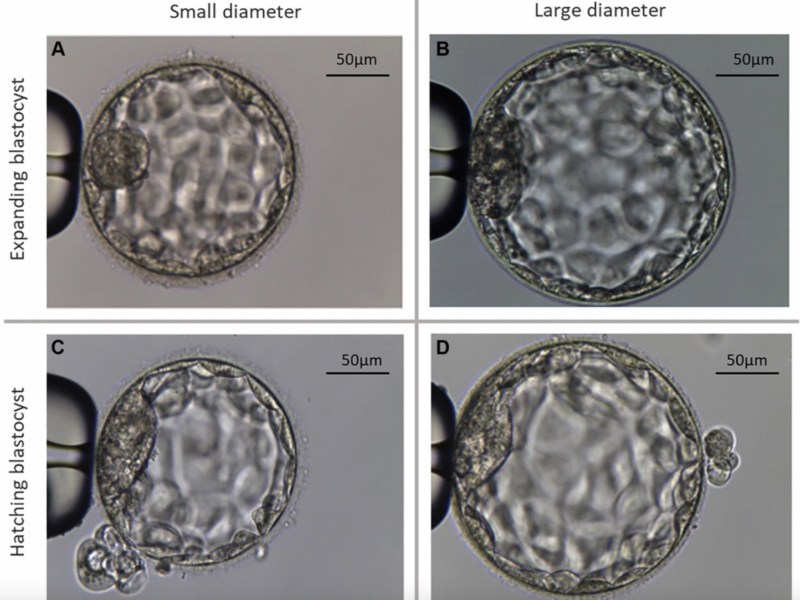
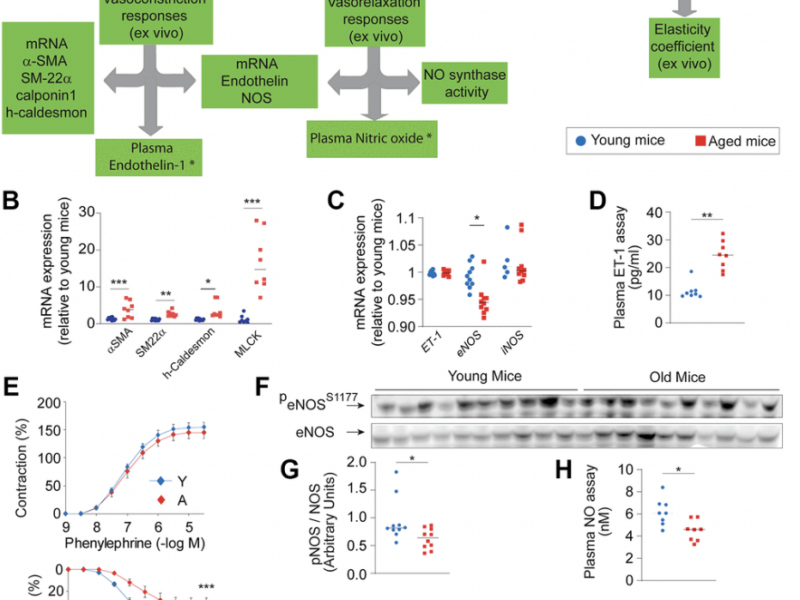
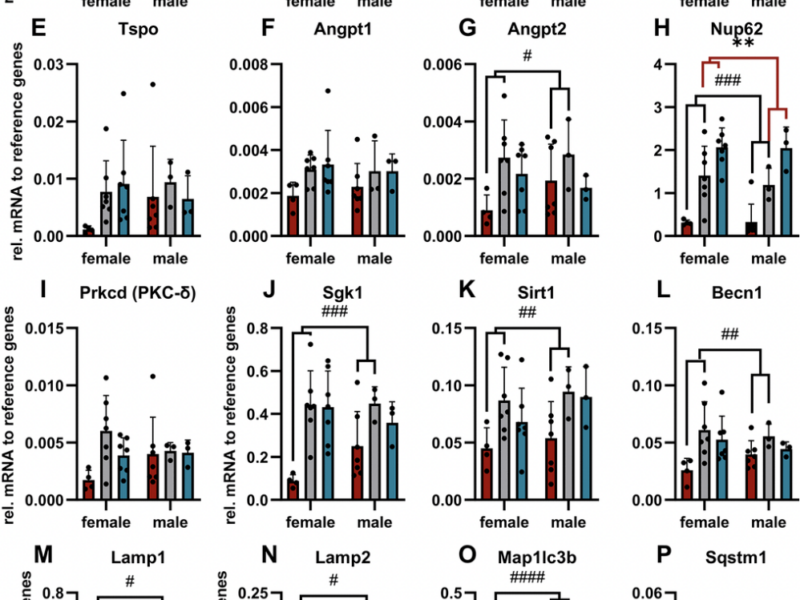
Aging (Aging-US) is pleased to announce a special Call for Papers for a commemorative collection honoring the legacy of Dr. Mikhail (Misha) Blagosklonny, the founding editor of the journal and a pioneer in aging biology.
Aging-US Research
Could a class of drugs that clear aging cells also help treat Alzheimer’s disease? A recent study, featured as the cover for Aging (Volume 17, Issue 3), titled “Differential senolytic inhibition of normal versus Aβ-associated cholinesterases: implications in aging and Alzheimer’s disease,” suggests they might—and with remarkable precision.
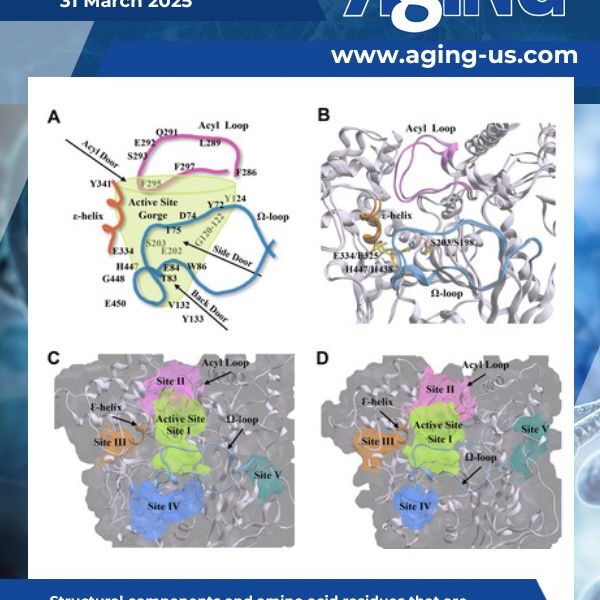
Cellular senescence is a hallmark of aging and the age-related condition, Alzheimer’s disease (AD). How senescence contributes to cholinergic and neuropathologic changes in AD remains uncertain. Furthermore, little is known about the relationship between senescence and cholinesterases (ChEs).

Could the air we breathe, the food we eat, or the chemicals in our everyday environment be accelerating our aging process? A recent study published in Aging suggests that exposure to certain environmental chemicals may be linked to faster biological aging through changes in DNA. These findings could have major implications for public health and longevity.
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, is a common treatment for cancer, but its effectiveness differs across patients. A recent study published as the cover for Volume 17, Issue 2 of Aging explored why this happens. The findings provide valuable insights, particularly for brain cancers like glioblastoma (GBM) and low-grade gliomas (LGG).
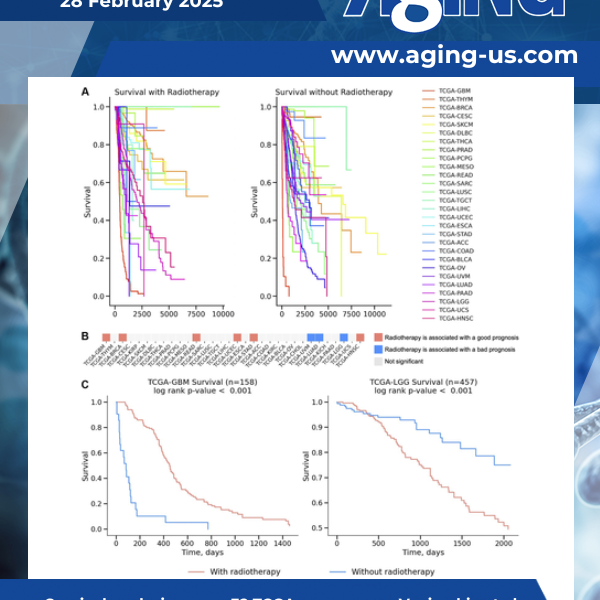
Radiotherapy is a crucial treatment option for various cancers. However, the results of radiotherapy can vary widely across different cancer types and even among patients with the same type of cancer. This variability presents a major challenge in optimizing treatment strategies and improving patient survival.