Aging-US Research

Treating aggressive cancers that do not respond to standard therapies remains one of the most significant challenges in oncology. Among these are basal-like breast cancers (BLBC), which lack hormone receptors and HER2 amplification. This makes them unsuitable for many existing targeted treatments. As a result, therapeutic options are limited, and patient outcomes are often poor.

The paper featured on the cover of this issue of Aging-US, published on October 30, 2025, entitled “SAMP-Score: a morphology-based machine learning classification method for screening pro-senescence compounds in p16-positive cancer cells,” represents an important methodological and conceptual advance at the interface of senescence biology, imaging and drug discovery.
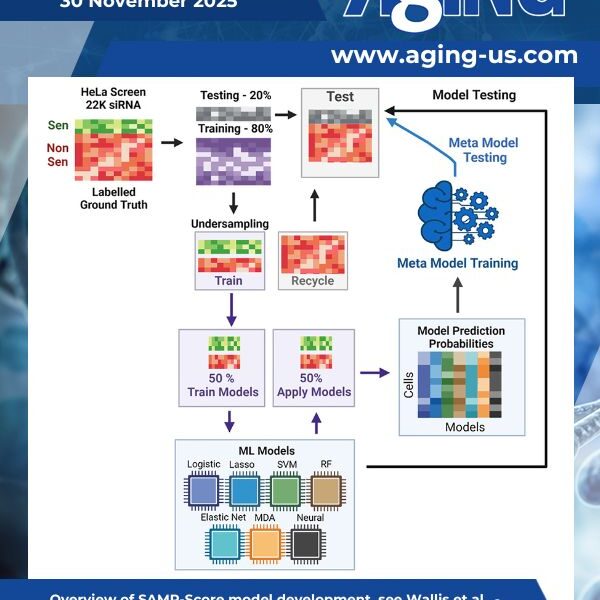
Senescence identification is rendered challenging due to a lack of universally available biomarkers. This represents a bottleneck in efforts to develop pro-senescence therapeutics – agents designed to induce the arrest of cellular proliferation associated with a senescence response in cancer cells for therapeutic gain.

Interest in healthier, longer lives is rising, supported by recent scientific advances in aging research. But turning those discoveries into everyday healthcare solutions remains a work in progress. In this landscape, longevity clinics have attracted attention as personalized alternatives to traditional medicine

Aging-US proudly sponsored the Future of Aging Research (FAR) Mixer 2025, hosted by the Aging Initiative on November 7 in Cambridge, MA, uniting students, researchers, and biotechnology leaders to advance aging research and shape a healthier, longer-lived future.

Synucleinopathies are a group of age-related neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy. Most individuals are not diagnosed until these diseases have significantly progressed, as early symptoms, such as a reduced sense of smell, subtle cognitive or motor changes are too vague to serve as reliable indicators.