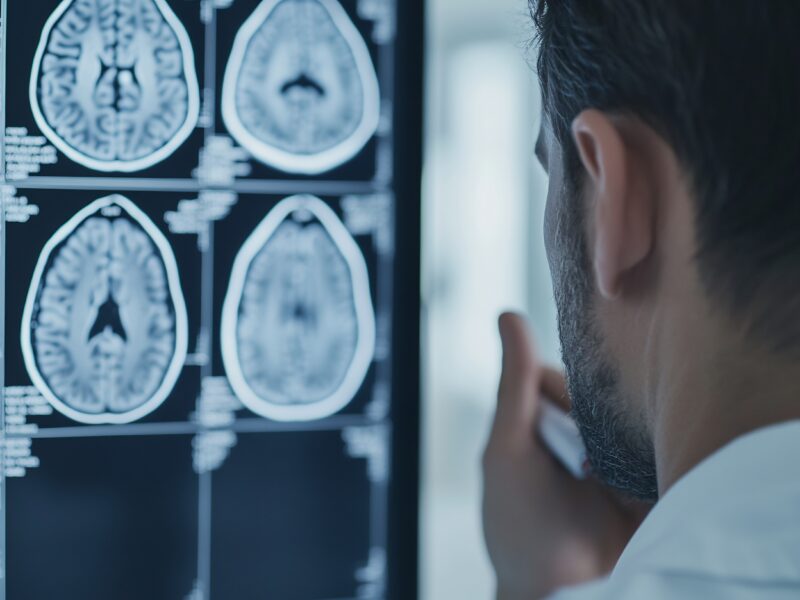
A new study published recently as the cover of Aging Volume 17, Issue 6, describes a new method to estimate how fast the brain is aging. By analyzing lipids, or fat molecules, in brain tissue, researchers from the National University of Singapore and Hanze University of Applied Sciences created a biological “clock” called DoliClock.
Aging (Aging-US) Research

Recent discoveries in aging research reveal a powerful insight: the biological changes that lead to chronic diseases begin far earlier than most people realize—often in midlife, well before symptoms appear. This early phase offers a valuable opportunity for prevention.
As we age, our brains become more sensitive to stress and disease. A recent study sheds light on a lesser-known risk: reduced oxygen levels.

In a world where we are living longer but not always healthier, scientists are searching for ways to add life to our years, not just years to our lives. A recent study published in Aging (Aging-US), Volume 17, Issue 4, led by researchers at the National University of Natural Medicine, suggests that certain common foods, already known for their health benefits, might also help slow or even reverse epigenetic or biological aging.

Werner syndrome is a rare condition marked by accelerated aging. A recent study, featured as the cover paper in Aging (Aging-US), Volume 17, Issue 4, led by researchers at the University of Oslo and international collaborators, suggests that nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a vital molecule involved in cellular energy production, may be key to understanding this disease and developing future strategies to manage it.

Aging (Aging-US) was proud to sponsor the Muscle Aging Science & Translation (MAST) Symposium, organized by the Aging Initiative at Harvard University on Friday, April 18, 2025. This important event brought together 350 participants—chosen from more than 1,300 applicants—including students, researchers, company founders, investors, and industry leaders.

Breast cancer survivors are living longer than ever, thanks to research and medical advances, but new studies suggest that some treatments may come with a hidden cost: accelerated aging. A recent study, titled “Accelerated aging associated with cancer characteristics and treatments among breast cancer survivors,” published in Aging (Aging-US), reveals that breast cancer and its treatments may speed up biological aging, with effects lasting up to a decade post-diagnosis.
Could a class of drugs that clear aging cells also help treat Alzheimer’s disease? A recent study, featured as the cover for Aging (Volume 17, Issue 3), titled “Differential senolytic inhibition of normal versus Aβ-associated cholinesterases: implications in aging and Alzheimer’s disease,” suggests they might—and with remarkable precision.

Could the air we breathe, the food we eat, or the chemicals in our everyday environment be accelerating our aging process? A recent study published in Aging suggests that exposure to certain environmental chemicals may be linked to faster biological aging through changes in DNA. These findings could have major implications for public health and longevity.
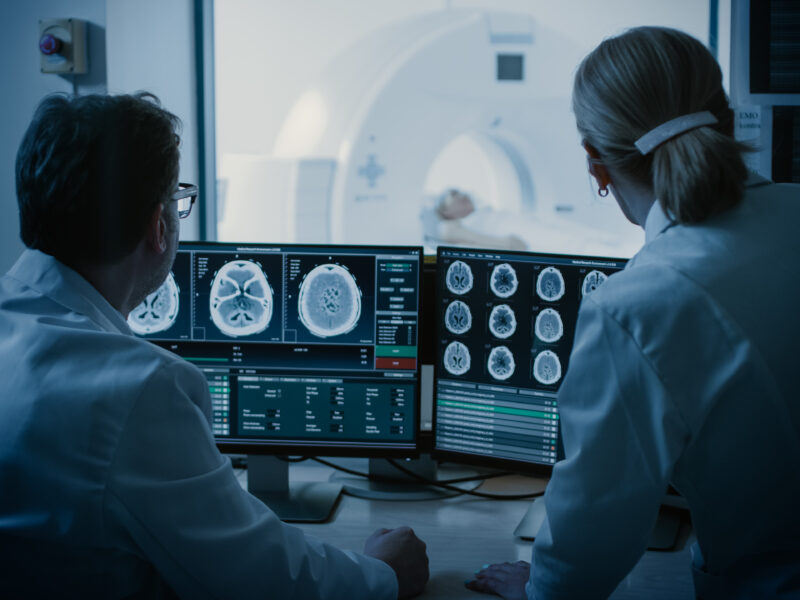
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, is a common treatment for cancer, but its effectiveness differs across patients. A recent study published as the cover for Volume 17, Issue 2 of Aging explored why this happens. The findings provide valuable insights, particularly for brain cancers like glioblastoma (GBM) and low-grade gliomas (LGG).