Synucleinopathies are a group of age-related neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy. Most individuals are not diagnosed until these diseases have significantly progressed, as early symptoms, such as a reduced sense of smell, subtle cognitive or motor changes are too vague to serve as reliable indicators.
Aging-US Research
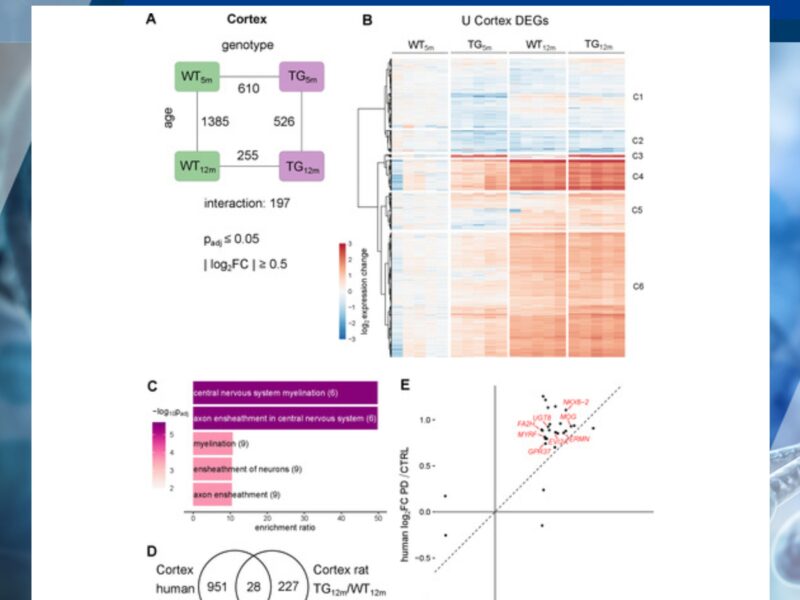
Synucleinopathies are age-dependent neurodegenerative diseases characterized by alpha-synuclein accumulation with distinct vulnerabilities across brain regions. Understanding early disease stages is essential to uncover initial molecular changes that might enable earlier diagnosis and causal therapy.

As people age, it is common to experience some memory lapses or slower thinking. Although this is often a normal part of aging, it can still affect a person’s quality of life. Scientists have been investigating ways to slow or prevent cognitive decline, and growing evidence points to the potential role of social interaction.

As life expectancy increases, there is growing interest not only in extending lifespan but also in improving the quality of those additional years. To address the physical and cognitive decline that often accompanies aging, researchers have explored a variety of strategies.

Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive lung disease that primarily affects people over the age of 60. It causes scarring in the lung tissue, which gradually reduces lung capacity and makes breathing difficult. Despite years of research, the exact causes of IPF remain largely unknown, and current treatments mainly aim to slow its progression rather than reverse or cure the disease.

As the global population grows older, understanding what drives the aging process is becoming increasingly important. Diseases like Alzheimer’s, cardiovascular conditions, and cancer are more common with age, yet many current treatments only manage symptoms rather than addressing the underlying biological causes.
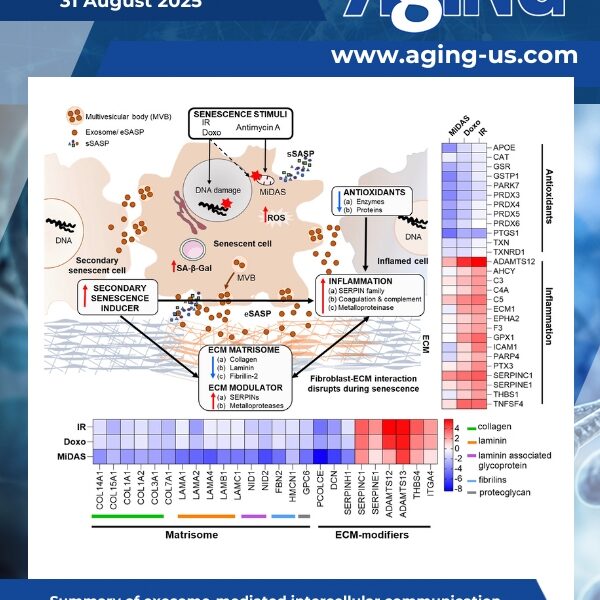
Senescence emerged as significant mechanism of aging and age-related diseases, offering an attractive target for clinical interventions. Senescent cells release a senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), including exosomes that may act as signal transducers between distal tissues, and propagate secondary senescence.

Researchers from Beiersdorf AG, Research and Development Hamburg in Germany, used a microphysiological co-culture system—a lab-based model simulating human circulation—to test the effects of young versus old blood serum on skin cells.

A new study published recently in Aging (Aging-US) Volume 17, Issue 6, examines a novel treatment for women with ovarian failure. Researchers from IVI Clinics Alicante in Spain investigated a procedure called Stem Cell Regenera, which uses the body’s own stem cells and platelet-rich plasma to activate dormant follicles in the ovaries.
A new study published recently as the cover of Aging Volume 17, Issue 6, describes a new method to estimate how fast the brain is aging. By analyzing lipids, or fat molecules, in brain tissue, researchers from the National University of Singapore and Hanze University of Applied Sciences created a biological “clock” called DoliClock.

