Could the air we breathe, the food we eat, or the chemicals in our everyday environment be accelerating our aging process? A recent study published in Aging suggests that exposure to certain environmental chemicals may be linked to faster biological aging through changes in DNA. These findings could have major implications for public health and longevity.
Aging (Aging-US) Research

Aging affects everyone differently. There are two types of aging: chronological aging, which refers to the number of years a person has lived, and biological aging, which reflects how well the body is functioning based on cellular changes. A recent study published as the cover for Volume 16, Issue 22 of Aging reports a new discovery that could revolutionize the way we understand aging and its impact on health.
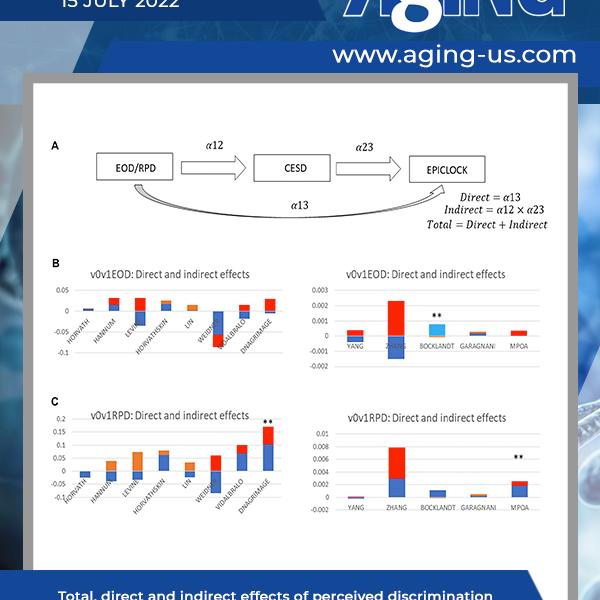
Background: Perceived discrimination may be associated with accelerated aging later in life, with depressive symptoms acting as potential mediator…


